13.10 The list type
append(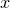 )
)
The append(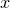 ) method appends the object
) method appends the object 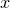 to a list and returns the new list.
to a list and returns the new list.
count(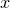 )
)
The count(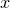 ) method returns the number of items in a list that equal
) method returns the number of items in a list that equal 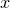 .
.
extend(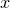 )
)
The extend(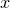 ) method appends the members of a list or vector
) method appends the members of a list or vector 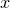 to the operand and returns the new list.
to the operand and returns the new list.
filter(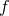 )
)
The filter(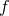 ) method takes a pointer to a function of one argument,
) method takes a pointer to a function of one argument, 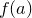 . It calls the function for every element of the list, and returns a new list of those elements for which
. It calls the function for every element of the list, and returns a new list of those elements for which 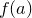 tests true.
tests true.
index(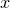 )
)
The index(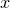 ) method returns the index of the first element of a list that equals
) method returns the index of the first element of a list that equals 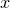 , or
, or 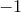 if no elements match.
if no elements match.
insert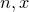 )
)
The insert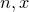 ) method inserts the number
) method inserts the number 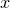 into a list at position
into a list at position 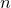 , and returns the new list.
, and returns the new list.
len()
The len() method returns the number of elements in a list.
map(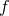 )
)
The map(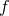 ) method takes a pointer to a function of one argument,
) method takes a pointer to a function of one argument, 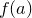 . It calls the function for every element of the list, and returns a list of the results.
. It calls the function for every element of the list, and returns a list of the results.
max()
The max() method returns the highest-valued item in a list.
min()
The min() method returns the lowest-valued item in a list.
pop()
The pop() method returns the last item in a list, and removes it from the list.
reduce(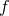 )
)
The reduce(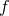 ) method takes a pointer to a function of two arguments. It first calls
) method takes a pointer to a function of two arguments. It first calls 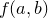 on the first two elements of the list, and then continues through the list calling
on the first two elements of the list, and then continues through the list calling 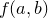 on the result and the next item in the list. The final result is returned.
on the result and the next item in the list. The final result is returned.
reverse()
The reverse() method reverses the order of the members of a list, and returns the new list.
sort()
The sort() method sorts the members of a list into ascending order, and returns the new list.
sortOn(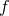 )
)
The sortOn(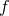 ) method sorts the members of a list using the user-supplied function
) method sorts the members of a list using the user-supplied function 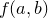 to determine the sort order.
to determine the sort order. 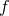 should return
should return 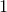 ,
, 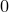 or
or 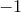 depending whether
depending whether 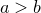 ,
, 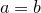 or
or 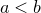 .
.
sortOnElement(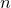 )
)
The sortOnElement(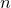 ) method sorts a list of lists on the
) method sorts a list of lists on the 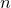 th element of each sublist. If
th element of each sublist. If 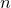 is negative, it counts from the final item of each list,
is negative, it counts from the final item of each list, 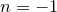 being the last item.
being the last item.
vector()
The vector() method returns the elements in a list as a vector.