6.3.6 List mapping and filtering
The methods filter(f), map(f) and reduce(f) can be used to perform actions on all of the members of a list in turn. filter(f) takes a function of one argument as its argument, and returns a new list of all of the members x of the original list for which f(x) tests true. For example:
pyxplot> txt = "once upon a time, there was a"
pyxplot> list = txt.split()
pyxplot> longWord(x) = x.len()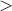 3
3
pyxplot> print list.filter(longWord)
["once", "upon", "time,", "there"]
The method map(f) also takes a function of one argument as its argument, and returns a list of the results f(x) for each of the members x of the original list. In other words, if f were sin, and the original list contained values of x, the result would be a list of values of sin(x). This example converts a list of numbers into Roman numerals:
pyxplot> factors = primeFactors(1001)
pyxplot> print factors
[7, 11, 13]
pyxplot> romanFactors = factors.map(romanNumeral)
pyxplot> print romanFactors
["VII", "XI", "XIII"]
The method reduce(f) takes a function of two arguments as its argument. It first calls 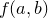 on the first two elements of the list, and then continues through the list calling
on the first two elements of the list, and then continues through the list calling 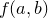 on the result and the next item in the list. The final result is returned:
on the result and the next item in the list. The final result is returned:
pyxplot> multiply(x,y) = x*y
pyxplot> factors = primeFactors(1001)
pyxplot> print factors.reduce(multiply)
1001