6.3.3 Sorting lists
Methods are provided for sorting data in lists. The simplest of these is the sort() method, which sorts the members into order of ascending value.1 The reverse() method can be used to invert the order of the list afterwards if descending order is wanted.
pyxplot> a = [8,4,7,3,6,2]
pyxplot> print a.sort()
[2, 3, 4, 6, 7, 8]
pyxplot> print a.reverse()
[8, 7, 6, 4, 3, 2]
Custom sorting
Often, however, a custom ordering is wanted. The sortOn(f) method takes a function of two arguments as its input. The function f(a,b) should return 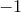 if a is to be placed before b in the sorted list,
if a is to be placed before b in the sorted list, 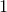 if a is to be placed after b in the sorted list, and zero if the two elements have equal ranking.
if a is to be placed after b in the sorted list, and zero if the two elements have equal ranking.
The cmp(a,b) function is often useful in making comparison functions for use with the sortOn(f) method: it returns either 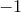 ,
, 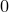 or
or 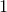 depending on Pyxplot’s default way of comparing two objects. In the example below, we pass it the magnitude of a and b to sort a list in order of magnitude.
depending on Pyxplot’s default way of comparing two objects. In the example below, we pass it the magnitude of a and b to sort a list in order of magnitude.
pyxplot> absCmp(a,b) = cmp(abs(a),abs(b))
pyxplot> a = range(-8,8)
pyxplot> print a
vector(-8, -7, -6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7)
pyxplot> a = a.list()
pyxplot> print a.sortOn(absCmp)
[0, -1, 1, -2, 2, -3, 3, -4, 4, -5, 5, -6, 6, -7, 7, -8]
pyxplot> print a.sort()
[-8, -7, -6, -5, -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
In this example, the range(start,end,step) function is used to generate a raster of values between 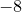 and
and 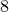 . It outputs a vector, which is converted into a list using the vector’s list() method. More information about vectors is in Section 6.5.
. It outputs a vector, which is converted into a list using the vector’s list() method. More information about vectors is in Section 6.5.
The subroutine command, which is often used to implement more complicated sorting functions, will be covered in Section 7.8. For example, the function used above could have been written:
subroutine absCmp(a,b)
{
return cmp(abs(a),abs(b))
}
Sorting lists of lists
The sortOnElement(n) method can be used to sort a list of lists on the 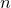 th sub-element of each sublist.
th sub-element of each sublist.
pyxplot> b = []
pyxplot> b.append([1797,1828,"Schubert"])
[[1797, 1828, "Schubert"]]
pyxplot> b.append([1770,1827,"Beethoven"])
[[1797, 1828, "Schubert"], [1770, 1827, "Beethoven"]]
pyxplot> b.append([1756,1791,"Mozart"])
[[1797, 1828, "Schubert"], [1770, 1827, "Beethoven"], [1756, 1791, "Mozart"]]
pyxplot> print b.sortOnElement(0) # Order of birth
[[1756, 1791, "Mozart"], [1770, 1827, "Beethoven"], [1797, 1828, "Schubert"]]
pyxplot> print b.sortOnElement(1) # Order of death
[[1756, 1791, "Mozart"], [1770, 1827, "Beethoven"], [1797, 1828, "Schubert"]]
pyxplot> print b.sortOnElement(2) # Alphabetical order
[[1770, 1827, "Beethoven"], [1756, 1791, "Mozart"], [1797, 1828, "Schubert"]]
Footnotes
- Non-numeric items are assigned arbitrary but consistent values for the purposes of sorting. Booleans are always lower-valued than numbers, but numbers are lower-valued than lists. Longer lists are always higher valued than shorter lists; larger dictionaries are always higher-valued than smaller dictionaries.